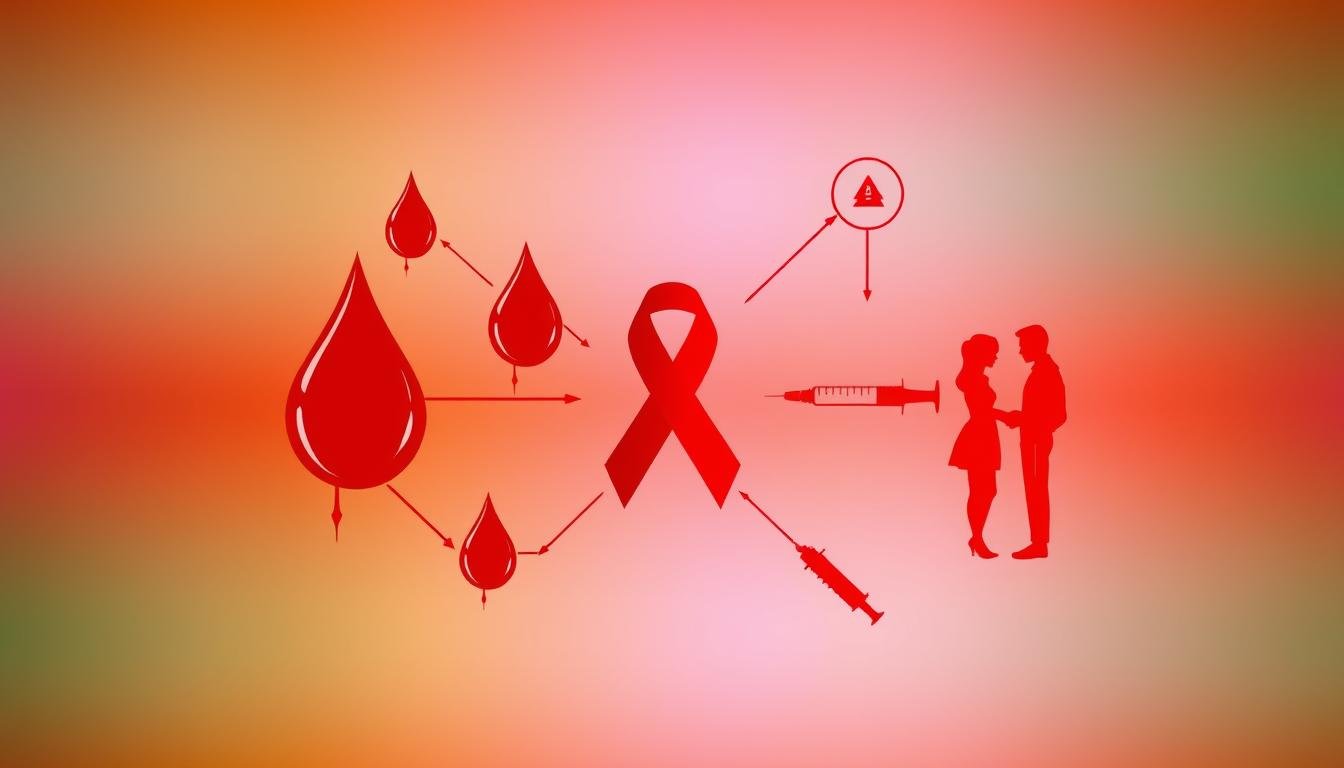
Approximately 38 million people around the world are currently living with HIV. In India, about 2.3 million cases have been reported. It’s vital to know how HIV spreads and the different ways it can be transmitted. The main ways HIV is passed on are through sex, blood contact, and from mother to child.
Key Takeaways
• Understanding how HIV is transmitted is crucial for prevention and awareness.
• HIV transmission methods include sexual contact, blood-to-blood contact, and mother-to-child transmission.
• Awareness of hiv transmission routes can help reduce the risk of transmission.
• Knowledge of HIV transmission is essential for developing effective prevention strategies.
• Understanding the basics of HIV transmission can help debunk common myths and misconceptions.
• Recognizing the importance of hiv transmission methods can help individuals take control of their health.
• Education and awareness about hiv transmission routes are key to preventing the spread of HIV.
The Basics of HIV Transmission
Knowing how HIV spreads is key to stopping it. The hiv spread mechanisms involve fluids like blood, semen, and breast milk. These fluids carry the virus. HIV attacks the immune system, mainly the CD4 cells.
The hiv infection pathways are complex. But they often involve direct contact with infected fluids. This can happen through sex, blood-to-blood contact, or from mother to child during pregnancy or breastfeeding. Misunderstandings about HIV can cause fear and stigma, making education vital.
In India and worldwide, the numbers are striking. India has about 2.1 million people living with HIV, with many new cases each year.More than 38 million people worldwide are living with HIV. Knowing how HIV spreads helps protect ourselves and others.
What is HIV, and How Does It Affect the Body?
HIV attacks the immune system. If untreated, it can lead to AIDS. AIDS weakens the immune system, making us more prone to infections and diseases.
Common Misconceptions About HIV Transmission
Many think HIV can spread through casual contact, like shaking hands or sharing food. But it only spreads through direct contact with infected bodily fluids.
Key Statistics in India and Globally
India has made strides in reducing new HIV cases. Yet, there’s more to do. Worldwide, the battle against HIV continues. Efforts focus on increasing access to prevention and treatment, especially in poorer countries.
Primary Routes of How HIV is Transmitted
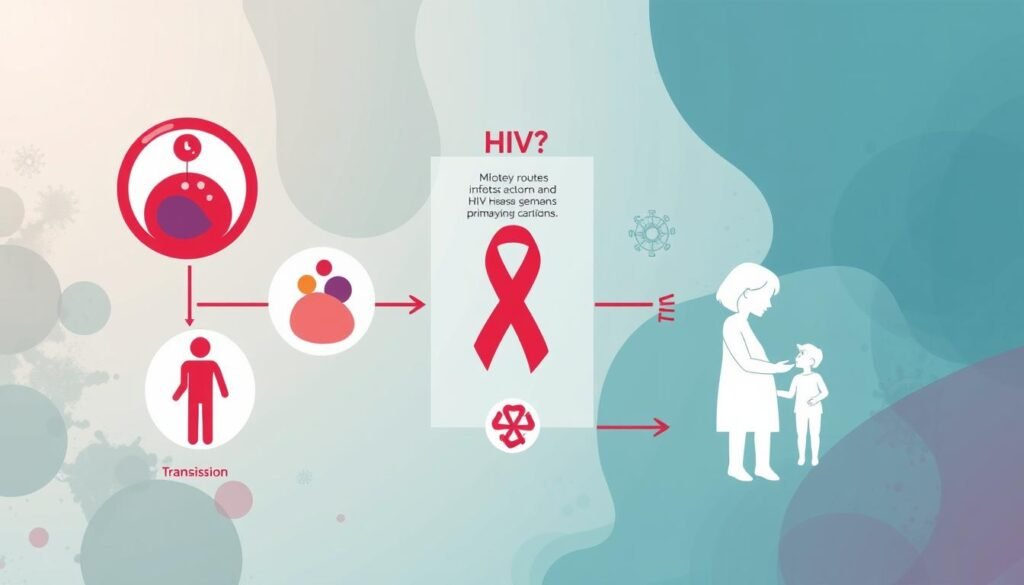
HIV spreads through several main ways. These include sexual contact, blood-to-blood contact, and from mother to child. Knowing these routes helps us understand how HIV spreads.
To stop HIV, it’s key to know how it’s transmitted. Safe practices like using condoms and not sharing needles can help. Also, HIV can spread through blood-to-blood contact, like in transfusions.
Sexual Transmission
Sexual contact is a common way HIV is spread. This happens during vaginal or anal sex without protection. Safe sex practices are crucial to lower the risk.
Blood-to-Blood Contact
Blood-to-blood contact is another main way HIV spreads. This includes sharing needles or getting transfusions. It’s important to avoid such contact to prevent HIV.
Mother-to-Child Transmission
Pregnant women with HIV face a risk of passing it to their babies. But, with the right treatment, this risk can drop. Knowing how HIV spreads helps prevent it.
Understanding HIV’s main ways of spreading helps us take steps to stop it. This includes safe sex, avoiding blood-to-blood contact, and getting medical help when needed. Together, we can fight HIV and make our community healthier.
| HIV Transmission Route | Risk Level | Prevention Methods |
| Sexual Transmission | High | Using condoms, getting tested regularly |
| Blood-to-Blood Contact equipment | High | Avoiding sharing needles, using sterile |
| Mother-to-Child Transmission anti retroviral therapy | Medium | Seeking medical care, taking anti retroviral therapy |
Risk Factors That Increase HIV Transmission
Understanding how HIV spreads is key to stopping it. Unprotected sex is a big risk because it lets the virus move from one person to another. Sharing needles or syringes for drugs is another risk, as it can spread infected blood.
To lower these risks, using hiv prevention methods is crucial. This includes wearing condoms, getting tested often, and not sharing needles. Also, giving antiretroviral therapy to pregnant women with HIV can stop the virus from passing to their babies.
Here are some key ways to reduce the risk of HIV transmission:
• Use condoms consistently and correctly
• Get tested for HIV regularly
• Avoid sharing needles or syringes
• Take antiretroviral therapy if living with HIV
By knowing these risks and taking steps to avoid them, people can lower their chance of getting HIV.
Regular testing and catching HIV early are vital. By testing often, people can find out if they have HIV and act to stop it from spreading. This is a big part of preventing hiv transmission and making sure those with HIV get the care they need.
| Risk Factor | Prevention Method |
| Unprotected sex | Use condoms consistently and correctly |
| Sharing needles | Avoid sharing needles or syringes |
| Mother-to-child transmission | Provide antiretroviral therapy to pregnant women living with HIV |
Body Fluids and Their Role in HIV Spread
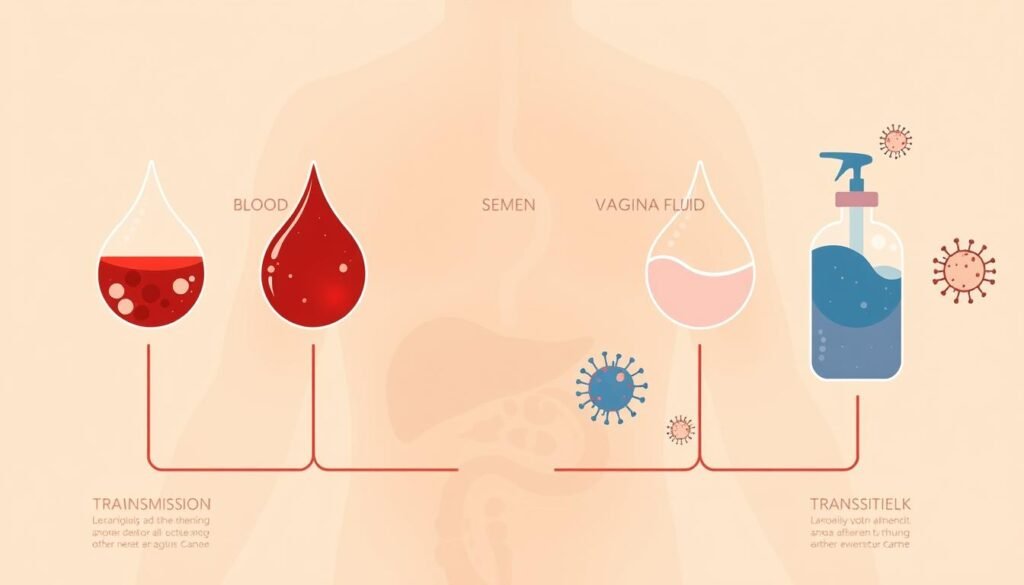
Knowing how HIV spreads through bodily fluids is key to stopping its spread. It’s important to grasp the facts about HIV transmission. Fluids like blood, semen, vaginal fluids, and breast milk can carry the virus.
Some bodily fluids are riskier than others when it comes to HIV. Blood and semen are high-risk because they have lots of the virus. But saliva, sweat, and tears are low-risk or no-risk because they rarely have enough virus to spread it.
High-Risk Fluids
• Blood
• Semen
• Vaginal fluids
• Breast milk
Low-Risk or No-Risk Fluids
• Saliva
• Sweat
• Tears
Understanding viral load is also crucial. It’s the amount of virus in bodily fluids. People with high viral loads are more likely to spread the virus. Taking antiretroviral therapy (ART) can lower viral load and prevent transmission.
By knowing how HIV is transmitted and taking precautions, we can lower our risk of getting it.
Medical and Healthcare Transmission Risks
In medical settings, HIV transmission methods can happen in different ways. This includes needlestick injuries and surgical procedures. To lower these risks, it’s important to follow strict guidelines. This includes using personal protective equipment (PPE) and safely handling and disposing of needles and sharp objects.
Some main hiv spread mechanisms in medical places are:
• Needlestick injuries: These happen when a healthcare worker gets pricked by a needle used on an HIV-positive patient.
• Surgical procedures: HIV can spread through surgeries if the right cleaning and disinfection steps aren’t taken.
• Blood transfusions: Although rare, HIV can spread through blood transfusions if the blood isn’t checked for the virus.
Healthcare workers need to know about these risks and how to prevent them. They should follow the right steps for handling needles and wear PPE. Also, they must make sure all medical tools are clean and disinfected.
Stopping HIV spread in medical places needs good protocols, education, and awareness. By knowing the risks and taking steps to reduce them, healthcare workers are key in stopping HIV spread.
Effective Methods for HIV Prevention
watch youtube video. Preventing HIV transmission needs a mix of methods. These include barrier protection, medications, and regular testing. Knowing these methods helps people protect their health and lower the risk of getting HIV.
Barrier Protection Methods
Barrier protection, like condoms, is very effective. They act as a physical barrier. This barrier stops HIV from passing from one person to another.
PrEP and PEP Medications
PrEP (Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis) and PEP (Post-Exposure Prophylaxis) are also key. These medicines can be taken daily or after exposure. They help prevent HIV from spreading.
Regular Testing and Early Detection
Regular testing and early detection are vital. By testing often, people can catch HIV early. This allows for quick treatment, which helps prevent it from spreading to others.
Using all these methods together helps prevent HIV. It’s important to know about these methods. Taking action to protect your health is crucial.
Debunking Myths About HIV Transmission
It’s key to know hiv transmission facts to stop the disease from spreading. Many myths and wrong ideas about how does hiv spread cause fear and stigma. We need to clear up these myths to spread awareness and education.
Some myths say HIV can spread through simple contact like shaking hands or sharing food and drinks. But this is not true. HIV mainly spreads through sexual transmission, blood-to-blood contact, and mother-to-child transmission. Also, HIV is not spread through hiv transmission facts like saliva, sweat, or tears.
• HIV is a virus that attacks and weakens the immune system.
• The virus spreads through certain bodily fluids, like blood, semen, and breast milk.
• Using protection, like condoms, can greatly lower the risk of transmission.
• Regular testing and knowing your status are key to preventing the disease’s spread.
By knowing the hiv transmission facts and how does hiv spread, we can fight stigma and support inclusivity. It’s vital to talk about this topic with care and respect, avoiding language that spreads myths. This way, we can build a supportive and informed community. Here, people can feel empowered to manage their health and well-being.
Conclusion: Taking Control of HIV Prevention
In the fight against HIV, knowing the facts is key. We can protect ourselves and others by understanding how HIV spreads. Using methods like barrier protection, PrEP, and regular tests are crucial.
Testing regularly helps catch HIV early. This means people can get treatment and stop it from spreading. Lowering risky behaviors and fighting stigma also helps a lot. Together, we can make HIV manageable, not a threat.
Knowledge is the first step to a safer world. Stay informed, practice prevention, and help end the HIV epidemic. Together, we can control HIV and build a better future for everyone.
FAQ
1.What is HIV and how does it impact the body?
Ans:-HIV attacks the immune system, focusing on CD4 cells. These cells help fight infections. As HIV destroys these cells, the immune system weakens. This weakens the body’s ability to fight off illnesses and infections.
2.What are the common misconceptions about HIV transmission?
Ans:-Many think HIV spreads through casual contact like sharing food or drinks. But this is not true. HIV mainly spreads through blood, semen, and vaginal fluids.
3. What are the primary routes of HIV transmission?
HIV spreads mainly through: 1. Sexual contact without protection. 2. Sharing needles or syringes. 3. It can be passed from a mother to her child during pregnancy or through breastfeeding.
4.What are the risk factors that increase HIV transmission?
Ans:-Risks include unprotected sex and sharing needles. Mother-to-child transmission is also a risk. Having STIs or risky sexual behaviors can increase transmission chances.
5. What is the role of bodily fluids in HIV transmission?
Ans:-Blood, semen, and vaginal fluids are high-risk for HIV. Saliva, tears, and sweat are much safer.
6. What are the medical and healthcare transmission risks for HIV?
Ans:-Healthcare workers face risks from needlestick injuries and surgeries. Following safety protocols is crucial to prevent HIV transmission.
7. What are the effective methods for HIV prevention?
Ans:-Effective prevention includes: 1. Using condoms and dental dams. 2. Taking PrEP and PEP medications. 3. Getting tested regularly to catch HIV early.
8. What are some common myths about HIV transmission?
Ans:-Myths say HIV spreads through mosquito bites or sharing food. But it mainly spreads through specific bodily fluids and risky behaviors.